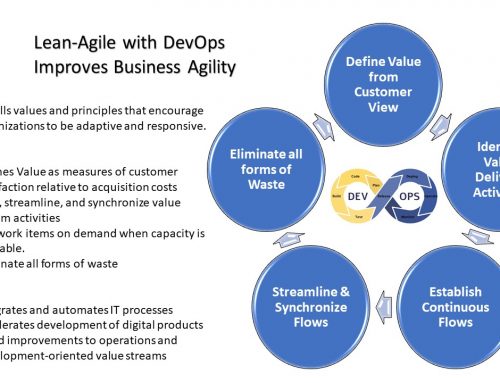
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving business landscape, the Power of Lean-Agile stands out as a transformative approach to achieving operational excellence and driving innovation. Lean and Agile methodologies, each with their own strengths, focus on eliminating waste and enhancing flexibility, respectively.
When integrated, they create a powerful synergy that enables organizations to streamline processes, respond swiftly to market changes, and continuously deliver value to customers.
In this blog, we will explore how combining Lean’s focus on efficiency with Agile’s adaptability can revolutionize project management, improve team dynamics, and propel your organization toward greater success.
Join us as we delve into the principles, benefits, and practical applications of Lean-Agile, and discover how this dynamic duo can unlock your organization’s full potential.
1. Understanding Lean and Agile Methodologies
Lean and Agile methodologies each offer unique but complementary approaches to improving organizational performance. Lean, originating from Toyota’s manufacturing practices, centers on maximizing value by systematically reducing waste and streamlining processes. Its core principles focus on eliminating non-value-added activities and continuously improving efficiency.
On the other hand, Agile, which emerged from the software development industry, emphasizes flexibility, iterative progress, and collaboration. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, prioritize customer feedback and adaptive planning to respond swiftly to changes and deliver incremental value.
Despite their distinct origins and focuses, both Lean and Agile share common goals of enhancing efficiency, responsiveness, and customer satisfaction, making their integration a powerful strategy for achieving operational excellence.
2. The Synergy of Lean and Agile
The synergy of Lean and Agile creates a potent combination that enhances both efficiency and adaptability within organizations. Lean’s focus on eliminating waste complements Agile’s iterative development by streamlining processes and ensuring that every step in a project adds value.
While Lean aims to remove non-essential activities and reduce inefficiencies, Agile introduces iterative cycles and continuous feedback, allowing for rapid adjustments and improvements. Together, these methodologies provide a framework where projects can be managed more effectively, products can be developed with greater responsiveness to customer needs, and teams can work more cohesively.
By integrating Lean’s waste-reduction principles with Agile’s flexibility, organizations can achieve streamlined workflows, quicker delivery times, and a more dynamic, collaborative environment, ultimately driving greater success and satisfaction across all levels.
3. Key Principles of Lean-Agile
The key principles of Lean-Agile combine the best aspects of both methodologies to drive operational excellence and responsiveness.
Value Stream Mapping is a crucial tool that helps organizations identify and optimize value streams by visualizing each step in a process, thereby eliminating waste and enhancing efficiency.
Iterative Development integrates Agile’s approach of breaking work into manageable sprints with Lean’s commitment to continuous improvement, enabling teams to make incremental changes and refine processes over time.
Customer Collaboration is another pivotal principle, where Agile’s focus on ongoing customer feedback complements Lean’s dedication to delivering maximum value, ensuring that products and services are continually aligned with customer needs and expectations.
Together, these principles foster a culture of continuous enhancement and responsiveness, driving greater efficiency and customer satisfaction.
4. Implementing Lean-Agile in Organizations
Implementing Lean-Agile in organizations involves several crucial steps to ensure a successful transition and sustained improvement.
Assessment and Planning are the initial stages, where organizations evaluate their existing processes to identify areas ripe for Lean-Agile adoption and develop a strategic plan for implementation. This involves mapping out current workflows, pinpointing inefficiencies, and setting clear objectives for integrating Lean and Agile principles.
Training and Culture Shift follow, requiring the education of teams on Lean-Agile methodologies and fostering a culture that embraces continuous improvement and adaptability. This cultural shift is essential for ensuring that all members of the organization are aligned with new practices and committed to ongoing development.
Finally, Tools and Techniques such as Scrum, Kanban, and Value Stream Mapping are employed to facilitate the practical application of Lean-Agile principles. Scrum and Kanban provide structured frameworks for managing workflows and iterating on tasks, while Value Stream Mapping helps visualize and optimize processes.
Together, these tools enable organizations to enhance efficiency, responsiveness, and collaboration, driving effective Lean-Agile implementation.
5. Case Studies and Success Stories
Case studies and success stories highlight the transformative impact of Lean-Agile practices across various industries. For instance, a major e-commerce company adopted Lean-Agile methodologies to streamline its product development processes, significantly reducing time-to-market and enhancing customer satisfaction through more responsive iterations.
Similarly, a leading healthcare provider implemented these practices to improve operational efficiency, resulting in faster patient care and reduced costs. These examples underscore that Lean-Agile practices can drive substantial improvements in efficiency and responsiveness across diverse sectors.
Key takeaways include the importance of aligning Lean-Agile strategies with organizational goals, investing in comprehensive training for team members, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration.
By learning from these success stories, organizations can better understand how to effectively integrate Lean-Agile principles, optimize their processes, and achieve meaningful results.
6. Challenges and Solutions
Implementing Lean-Agile practices often comes with challenges such as resistance to change, integration issues, and maintaining momentum.
Resistance to change can arise when employees are accustomed to traditional workflows and may be skeptical of new methodologies. To address this, it’s crucial to communicate the benefits of Lean-Agile clearly, involve team members in the transition process, and provide ongoing support and training.
Integration issues might occur when aligning Lean-Agile practices with existing systems or processes, which can be mitigated by piloting the approach in smaller, manageable segments and gradually scaling up based on feedback and results.
Maintaining momentum can be challenging as initial enthusiasm wanes, so it’s important to celebrate early wins, continuously track progress, and keep the focus on the long-term benefits.
By employing these strategies—emphasizing communication, phased implementation, and regular reinforcement—organizations can effectively overcome these obstacles and ensure a successful Lean-Agile adoption.
7. The Future of Lean-Agile
The future of Lean-Agile is set to be influenced by several emerging trends and innovations that are reshaping how organizations implement these methodologies.
Emerging trends include the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance decision-making and streamline processes.
The rise of remote and hybrid work models is also prompting adaptations in Lean-Agile practices to support virtual collaboration and distributed teams.
Predictions for evolution suggest that Lean-Agile will continue to evolve towards even greater adaptability and real-time responsiveness, with an emphasis on integrating continuous delivery pipelines and real-time data analytics.
This evolution will enable organizations to stay competitive by rapidly adapting to market changes and customer needs, ultimately driving more agile and efficient operations.
As these trends unfold, Lean-Agile practices will become increasingly dynamic, offering new ways to enhance performance and achieve strategic goals in a rapidly changing business landscape.
In conclusion, the integration of Lean and Agile methodologies offers a powerful approach to enhancing organizational efficiency and adaptability.
By combining Lean’s focus on waste reduction with Agile’s iterative development, organizations can achieve streamlined processes, faster response times, and a more collaborative work environment. We encourage you to explore Lean-Agile principles to unlock these benefits and drive continuous improvement within your teams.
Start by integrating Lean-Agile practices into your workflows and seek out additional resources and training to support your journey. Embracing these methodologies will not only optimize your operations but also empower your organization to thrive in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Was this article valuable to you?
(Please rate from 1 to 5)
1 – Not at all
2 – Slightly
3 – Neutral
4 – Valuable
5 – Extremely valuable